Page 28 - 048
P. 28
10
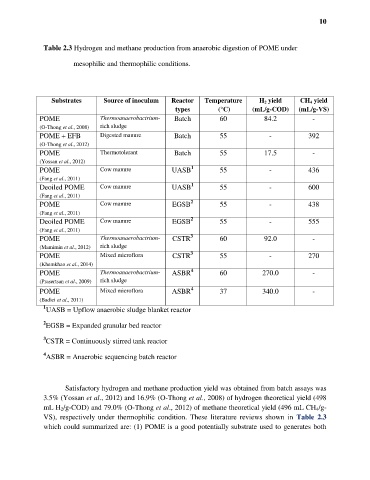
Table 2.3 Hydrogen and methane production from anaerobic digestion of POME under
mesophilic and thermophilic conditions.
Substrates Source of inoculum Reactor Temperature H 2 yield CH 4 yield
types (°C) (mL/g-COD) (mL/g-VS)
POME Thermoanaerobactrium- Batch 60 84.2 -
(O-Thong et al., 2008) rich sludge
POME + EFB Digested manure Batch 55 - 392
(O-Thong et al., 2012)
POME Thermotolerant Batch 55 17.5 -
(Yossan et al., 2012)
1
POME Cow manure UASB 55 - 436
(Fang et al., 2011)
1
Deoiled POME Cow manure UASB 55 - 600
(Fang et al., 2011)
2
POME Cow manure EGSB 55 - 438
(Fang et al., 2011)
2
Deoiled POME Cow manure EGSB 55 - 555
(Fang et al., 2011)
3
POME Thermoanaerobactrium- CSTR 60 92.0 -
(Mamimin et al., 2012) rich sludge
3
POME Mixed microflora CSTR 55 - 270
(Khemkhao et al., 2014)
4
POME Thermoanaerobactrium- ASBR 60 270.0 -
(Prasertsan et al., 2009) rich sludge
4
POME Mixed microflora ASBR 37 340.0 -
(Badiei et al., 2011)
1
UASB = Upflow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor
2
EGSB = Expanded granular bed reactor
3
CSTR = Continuously stirred tank reactor
4
ASBR = Anaerobic sequencing batch reactor
Satisfactory hydrogen and methane production yield was obtained from batch assays was
3.5% (Yossan et al., 2012) and 16.9% (O-Thong et al., 2008) of hydrogen theoretical yield (498
mL H 2/g-COD) and 79.0% (O-Thong et al., 2012) of methane theoretical yield (496 mL CH 4/g-
VS), respectively under thermophilic condition. These literature reviews shown in Table 2.3
which could summarized are: (1) POME is a good potentially substrate used to generates both