Page 31 - 048
P. 31
13
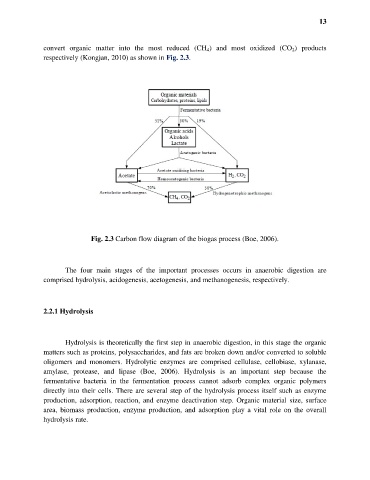
convert organic matter into the most reduced (CH 4) and most oxidized (CO 2) products
respectively (Kongjan, 2010) as shown in Fig. 2.3.
Fig. 2.3 Carbon flow diagram of the biogas process (Boe, 2006).
The four main stages of the important processes occurs in anaerobic digestion are
comprised hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis, respectively.
2.2.1 Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is theoretically the first step in anaerobic digestion, in this stage the organic
matters such as proteins, polysaccharides, and fats are broken down and/or converted to soluble
oligomers and monomers. Hydrolytic enzymes are comprised cellulase, cellobiase, xylanase,
amylase, protease, and lipase (Boe, 2006). Hydrolysis is an important step because the
fermentative bacteria in the fermentation process cannot adsorb complex organic polymers
directly into their cells. There are several step of the hydrolysis process itself such as enzyme
production, adsorption, reaction, and enzyme deactivation step. Organic material size, surface
area, biomass production, enzyme production, and adsorption play a vital role on the overall
hydrolysis rate.