Page 97 - 048
P. 97
☺
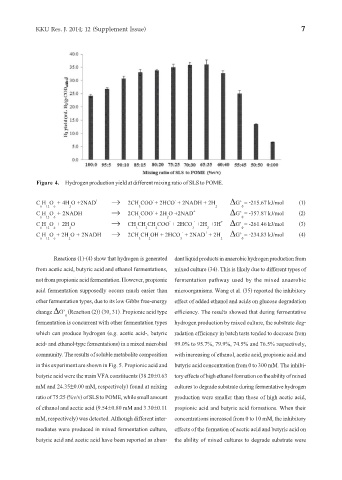
Figure 4. Hydrogen production yield at different mixing ratio of SLS to POME.
C H O + 4H O +2NAD + → 2CH COO + 2HCO + 2NADH + 2H 2 ΔG’ = -215.67 kJ/mol (1)
-
-
3
2
0
6 12 6
C H O + 2NADH → 2CH COO + 2H O +2NAD + ΔG’ = -357.87 kJ/mol (2)
-
6 12 6
0
2
3
C H O + 2H O → CH CH CH COO + 2HCO +2H +3H + ΔG’ = -261.46 kJ/mol (3)
-
-
2
2
3
2
0
2
3
6 12 6
+
-
C H O + 2H O + 2NADH → 2CH CH OH + 2HCO + 2NAD + 2H ΔG’ = -234.83 kJ/mol (4)
6 12 6 2 3 2 3 2 0
Reactions (1)-(4) show that hydrogen is generated dant liquid products in anaerobic hydrogen production from
from acetic acid, butyric acid and ethanol fermentations, mixed culture (34). This is likely due to different types of
not from propionic acid fermentation. However, propionic fermentation pathway used by the mixed anaerobic
acid fermentation supposedly occurs much easier than microorganisms. Wang et al. (35) reported the inhibitory
other fermentation types, due to its low Gibbs free-energy effect of added ethanol and acids on glucose degradation
change ΔG’ (Reaction (2)) (30, 31). Propionic acid type efficiency. The results showed that during fermentative
0
fermentation is concurrent with other fermentation types hydrogen production by mixed culture, the substrate deg-
which can produce hydrogen (e.g. acetic acid-, butyric radation efficiency in batch tests tended to decrease from
acid- and ethanol-type fermentations) in a mixed microbial 99.0% to 95.7%, 79.9%, 74.5% and 76.5% respectively,
community. The results of soluble metabolite composition with increasing of ethanol, acetic acid, propionic acid and
in this experiment are shown in Fig. 5. Propionic acid and butyric acid concentration from 0 to 300 mM. The inhibi-
butyric acid were the main VFA constituents (38.20±0.63 tory effects of high ethanol formation on the ability of mixed
mM and 24.35±0.00 mM, respectively) found at mixing cultures to degrade substrate during fermentative hydrogen
ratio of 75:25 (%v/v) of SLS to POME, while small amount production were smaller than those of high acetic acid,
of ethanol and acetic acid (9.54±0.80 mM and 3.30±0.11 propionic acid and butyric acid formations. When their
mM, respectively) was detected. Although different inter- concentrations increased from 0 to 10 mM, the inhibitory
mediates were produced in mixed fermentation culture, effects of the formation of acetic acid and butyric acid on
butyric acid and acetic acid have been reported as abun- the ability of mixed cultures to degrade substrate were