Page 79 - 048
P. 79
61
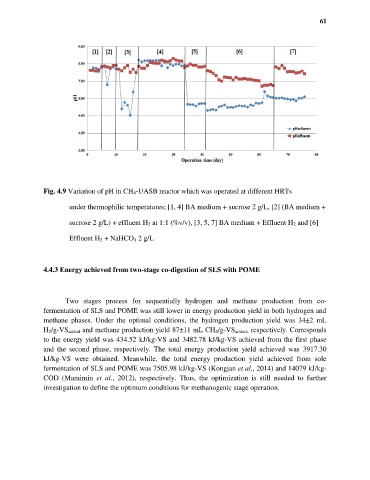
Fig. 4.9 Variation of pH in CH 4-UASB reactor which was operated at different HRTs
under thermophilic temperatures; [1, 4] BA medium + sucrose 2 g/L, [2] (BA medium +
sucrose 2 g/L) + effluent H 2 at 1:1 (%v/v), [3, 5, 7] BA medium + Effluent H 2 and [6]
Effluent H 2 + NaHCO 3 2 g/L
4.4.3 Energy achieved from two-stage co-digestion of SLS with POME
Two stages process for sequentially hydrogen and methane production from co-
fermentation of SLS and POME was still lower in energy production yield in both hydrogen and
methane phases. Under the optimal conditions, the hydrogen production yield was 34±2 mL
H 2/g-VS added and methane production yield 87±11 mL CH 4/g-VS added, respectively. Corresponds
to the energy yield was 434.52 kJ/kg-VS and 3482.78 kJ/kg-VS achieved from the first phase
and the second phase, respectively. The total energy production yield achieved was 3917.30
kJ/kg-VS were obtained. Meanwhile, the total energy production yield achieved from sole
fermentation of SLS and POME was 7505.98 kJ/kg-VS (Kongjan et al., 2014) and 14079 kJ/kg-
COD (Mamimin et al., 2012), respectively. Thus, the optimization is still needed to further
investigation to define the optimum conditions for methanogenic stage operation.